Future Imperfect - Action Cards
Action cards are at the heart of Future Imperfect. Whenever success is in doubt, action cards will help you determine the result. In this section action card usage will be explained in a step by step manner. For further information about card anatomy, card creation or alternative card usages, see Future Imperfect: Appendix - 1, Action Cards.
Contents
- 1 The Basics
- 2 Combat Actions
The Basics
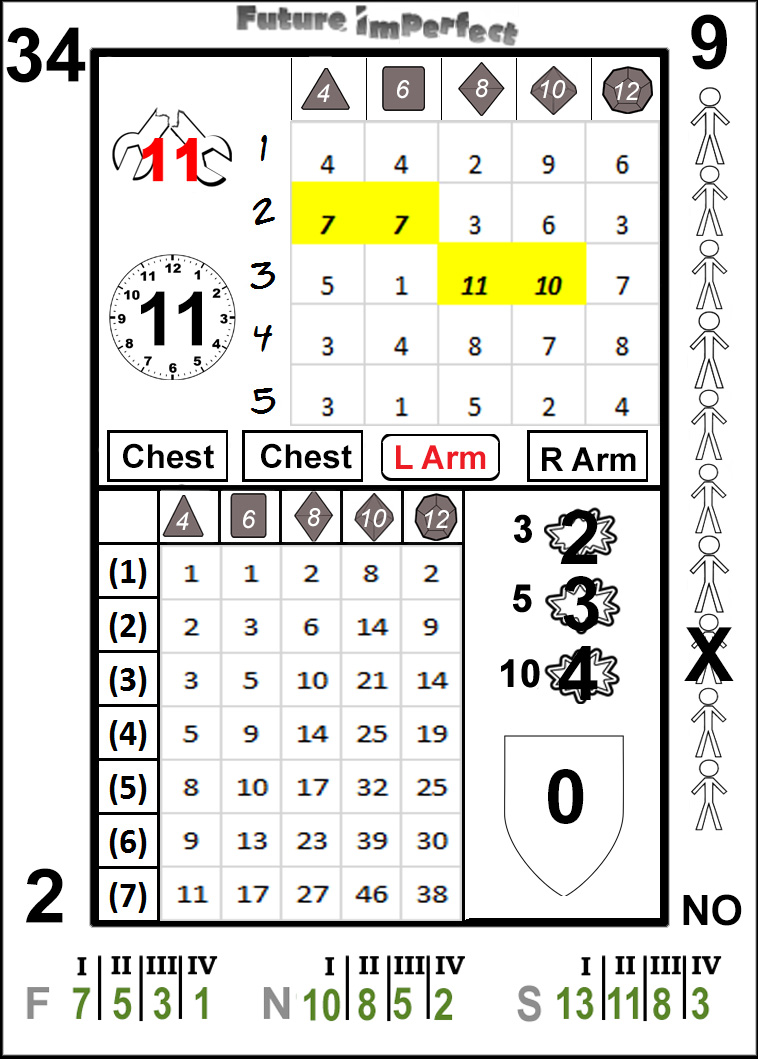
The Action Cards included with Future Imperfect are loaded with data. The sheer density of information may seem daunting at first, yet once their usage is mastered they become simple and quick to utilize. Note that even in the most detailed of actions only a subset of the information contained will be referenced. In most cases only one or two sections will be necessary.
Begin by drawing a card and glancing at the face.
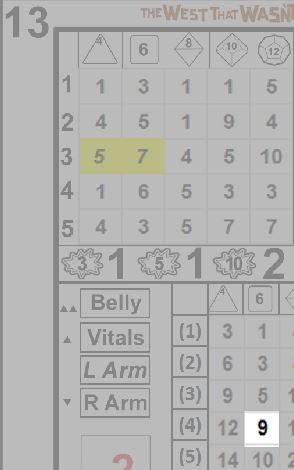
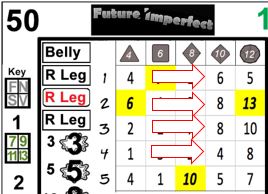
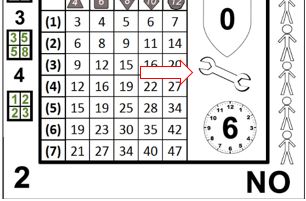
The example card here is number 34. When cards are referenced, the large number in the upper left is the unique identifying number. Since the deck has 54 cards, the cards are numbered 0-53. The numbers in the upper right range from 0-14, with 4 each of 1-13, and one each of 0 and 14. The numbers in the lower left range from 0-5, with 13 each of 1-4, and one each of 0 and 5. The lower right contains yes and no, with 27 of each. Using these card entries is detailed in another section, while the logic behind their distribution is contained in the appendix referenced above.
The Cause Grid: Simple Skill Checks
Skill checks can be performed using only a single result from the card. In the upper section of the card is a 5x5 grid, with rows numbered from 1-5, and columns with 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12, along with symbols matching the shape of dice with the given number of sides.
Do not worry, dice never need to be rolled in conjunction with action cards.
Then why are the dice symbols present? As a player of roleplaying games, you are likely familiar with polyhedral dice. If this is your first roleplaying game, you may have seen the 6 sided cube that is used in table games such as craps to board and roleplaying games like Monopoly and Dungeons & Dragons as well. The dice symbols help to set expectations for players on what results are likely to occur in a given column. The 6 column, for example, acts like the standard six sided cube. Most results in the 6 column will fall within the range of 1-6, while the results in the 10 column will fall mostly from 1-10. A full explanation for how the results are distributed is available in the appendix linked above.
Each row is an additional die of the appropriate type. When a skill level is greater than one, the player resolving the action may choose any result from a row equal to or less than the level of the skill, in the appropriate column based on the governing trait. The only exception to this is critical failures, discussed in the special section below. For example, if Sid Scorpio has an Essence of d6, and a Bravery of 3, he may choose either 6, 1 or 1 (assuming card 34, above, as the card drawn).
Skill checks are that simple. Draw a card, cross-reference the die type of the appropriate trait with the skill level of the skill being used, and choose the result. In general, the highest result present will be chosen, though there may be reasons why another result is selected. Except in the case of critical failures the active player (the one that drew the card and is resolving the check) may always choose whichever result he wishes.
After completing the check, place the card in the discard pile. Even though only a subset of the information on the card was used, each card is utilized for a single action only. In the case of a simple skill check, from 1-5 rows in a single column will be consulted, nothing more.
Further Examples
Fill this section with more examples of simple skill checks.
Exceptional Results
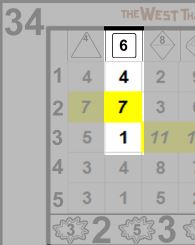
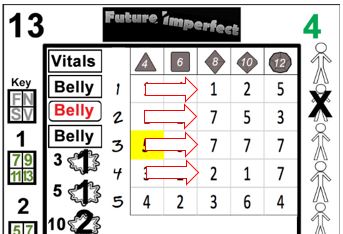
Great stories are filled with instances of characters performing extraordinary actions. Future Imperfect seeks to simulate this with extraordinary results. Previously, it was mentioned that most results in a given column will fall between 1-n, where n is the number displayed atop the column. In some cases, results that are equal to or greater than that number will be shaded in yellow, bold and italicized*. These are exceptional results.
Exceptional results allow results to be open ended. When one of the squares in the result set meet the criteria above, immediately draw another card and add the value from the corresponding square to the previous result. If another exceptional result is drawn, repeat the procedure until a standard result is drawn.
Unlike standard skill checks, exceptional results use the exact cell only, lower results may not be selected. In other words if the exceptional result is in 2-10 (as in 34, above), then only the 2-10 result in the next card may be chosen. If multiple cells within the result set display exceptional results, either may be selected after drawing the new card.
Exceptional results are optional.
*See the Appendix referenced above for the rationale behind the symbology.
Exceptional Results, Example 1: Sid being Sid
Sid Scorpio (played by Sid...seriously) is attempting to elude 3 GPR commissars who wish to question him after his baggage was searched and found to contain a coagulator, contraband on this planet. He has just exited the spaceport, and is looking for the fastest route to anywhere but here. With the commissars hot on his trail, he knows that his situation is desperate so he decides to attempt something truly crazy (well, crazy for someone who isnt Sid Scorpio...). He runs along the arrivals path and leaps up, attempting to grab the bumper of a passing hover taxi.
The Master declares this to be an incredibly difficult task, and assigns a TN of 11. Sid just smiles and says, "Its in the bag." He draws a card.
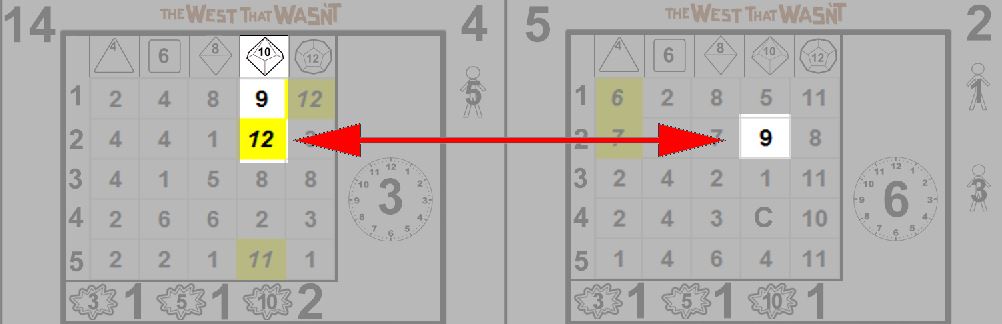
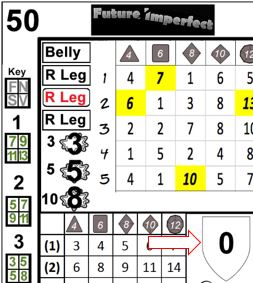
Sid Scorpio has a Dexterity of 2d10. Consulting the card drawn, 34, he finds 7 and 10, the latter denoting an exceptional result. "See, I told you.", says Sid (the player), and he draws another card, 10. Cross referencing the 2-10 result he finds a 9, making his total 19.
"Piece of cake" Sid grabs the bumper, looks back at the commissars, smiles and winks. "Too-da-loo, gents."
Note: If optional rules for bumps were used, he would have achieved 2. See the section on bumps, below.
Exceptional Results, Example 2: Xenes Does the Heavy Lifting
Back on the Ball Lightning, Xenes (played by Eric) learns that Sid was caught trying to smuggle a coagulator past customs. "Unbelievable", he thinks to himself. Since Sid is a member of the crew of this vessel, his crime could prevent them from leaving spacedock, and could also cause the captain unnecessary grief from the planetary government. Xenes, never a fan of the GPR, figures that it is in the best interest of all concerned to use the shipboard computer to quickly hack in to the spaceport computer and erase the record before it gets in front of too many prying eyes.
Even though the Ball Lightning has a very powerful computer, spaceport security is tight and vigilant. The Master declares the TN a near-impossible 13. Eric nods and draws a card, 34.
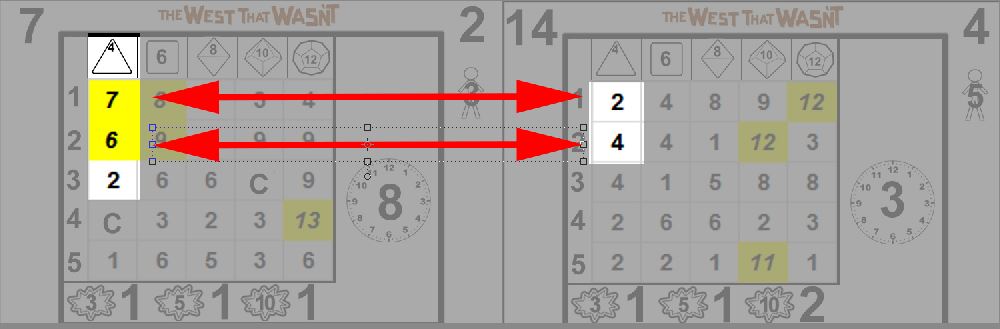
Xenes has 4d10 in CompTech: Hacking. Glancing over the results, he is pleased to find 7, 10, 3 and 7, including an exceptional result. "This just might work", says Eric as he draws another card, 11. Fortuitously, another exceptional result! Drawing again, he reveals the 10. Adding the results gives an incredible 30. Click, click, delete.
Note that even though Xenes has a 4d10 in Hacking, he cannot choose the 11 exceptional result on the 10 card, because only the 2-10 cell can be used in this draw. Also, even though the 4-10 result in card 10 is CF, and his skill is 4d10, this does not cause a critical failure. Critical failures can only occur on the card drawn to resolve the action, the additional cards drawn for the exceptional result are optional, and only serve to extend the initial card. This also explains why only the 2-10 cell is relevant, in effect only that die is rolled, no further action is attempted.
Finally, if the optional bump rules (see below) were being used, Xenes would have generated a whopping 4 bumps!
Exceptional Results, Example 3:
Somebody has a 4d4 in something. They attempt it and see exceptional results in 1 and 4. They draw a second card and total results, getting 6 and 10. They choose 10. Example over.
Critical Failures
As with exceptional successes, entertaining stories often include spectacular failures. At times even the most skilled individual encounters a set of circumstances that cannot be resolved satisfactorily. Critical failures are results that lead to failure no matter the situation, and often can lead to the most dramatic result possible. Adjudicating critical failures is covered in section, this paragraph is solely concerned with how to read the results on the action card.
In most checks, the player can select any result in the appropriate column up to and including the row of the skill level being utilized. The exception to this is when the exact row/column combination yields a CF result. Note that it does not matter if a CF is in any other location on the card, a critical fail only occurs if the exact box directed by the attribute/skill combination on the resolution card* contains CF.
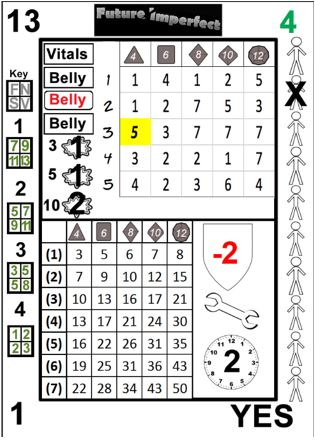
In the given card image below, if Chuk has a 4d12 Strength, and is attempting to lift a heavy bulkhead, he would critically fail. In the event of a critical fail the Master determines a result appropriate to the situation at hand, however any member of the Crew, including the player resolving the card, may make suggestions.
*In Future Imperfect, all actions can be resolved by a single card draw. This card is called the resolution card. Some optional effects, such as exceptional results, can trigger further draws. These draws extend the result on the resolution card, and are never counted for critical failures in any way.
Complex Skill Checks: More Than a Binary Result
In some cases, an action requires more than a pass or fail. These actions are called complex skill checks. The check generates a binary pass/fail, and if successful, a magnitude defining how successful the action was.
These types of checks could be due to extended actions (where success is achieved over time such as defeating a complex security system), contests (where two characters compete at a task), actions involving a magnitude rather than a binary success (such as throwing an item for distance), combat actions, or other possibilities as defined by the Master. Complex skill checks take simple skill checks one step further, and use two sections of the card: the cause grid (like simple skill checks) and the effect grid.
As with simple skill checks, the cause grid is used to determine whether an action is a success. The effect grid is used to determine the magnitude, if necessary. Without a success, no magnitude is generated. An action card is discarded after one resolution (successful or not).
Using the Effect Grid
Unlike the cause grid, the results in the effect grid are always arranged in order of increasing value as the row increases. The rationale for the arrangement of values in the grids is covered in the appendix linked above. Because of this, the cell corresponding to the appropriate row and column is always chosen.
Generating Victories
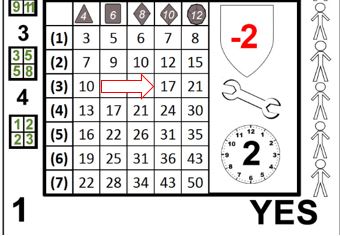
The value in the given cell is the magnitude of the action, but this by itself does not provide all of the information needed. Victory has a target of 6. This means that for each multiple of 6* in the magnitude, one victory is generated. For example, in the 34 card (below), the (2)d6 effect grid result would generate one victory, because the magnitude is 8. Unless specified otherwise, any amount over the target is lost, in this case, 2.
When performing a complex action that requires multiple victories, the Master will inform the player of the required number of victories before they make their attempt.
*See the appendix linked above for more on the target magnitude of 6.
Complex Skill Checks, Example 1: Kayla Argent Disables a Force Field
After spending the night moving carefully through Azuriach held ground, Kayla has determined that her compatriot Oso is being detained in a subterranean cell beneath a guard tower. She knows the tower is protected by a force field, so her only hope of gaining access and freeing Oso requires finding an access panel and disabling the field. Utilizing her trademark patience and precision, she systematically narrows the possible locations to a single wall section, and deftly approaches the hidden access panel.
After opening the panel, she assess the security system and determines that it is a difficult and potentially time consuming operation. Just then, she hears the door at the top of the stairs open, and two sets of footsteps are descending toward her. The Master informs her that it will require 5 victories to disable the alarm. The security system is TN 7. She draws the following card:
Kayla has 4d8 in Security Systems, and she is using a TL 8 encryption/decryption scope (3)d10. Consulting the card, she finds that she has succeeded (1, 7, 7, 2 vs TN 7).
Excellent. Now to determine how much progress is made this round.
The quality of the equipment, (3)d10, is used to generate the effect. Rats! With the standard effect threshold of 6, the 17 magnitude generates only two victories. A single point more and 3 victories would have been scored. Note that unlike reading the cause grid, in the effect grid only the exact cell referenced is necessary.
Not quite halfway there, Kayla knows she needs to step up her game if she is to deactivate the field quickly enough to be able to handle the approaching guards as well.
Complex Skill Checks, Example 2:
Combat Actions
Combat actions can potentially use the entire action card. Each section will be covered individually, in sequence, with mini-examples. At the conclusion of the section a full example will be illustrated.
Resolution Flow
The order of operations is similar to other games:
1. Determine hit or miss. If miss, proceed to step 6.
2. Determine number of hits.
3. Determine hit location(s).
4. Check for armor penetration/ablation. If no penetration, proceed to step 6.
5. Determine damage.
6. Check for ancillary effects.
All results are found on a single card. At the conclusion of the resolution, discard the card.
Determining Hits
In combat, hits are determined exactly like simple skill checks. In ranged combat, the TN is determined by the range and weapon type, and modified based on environmental, equipment and other factors as determined by the Master. In melee combat, the TN is determined by weapon type and skill of the opponent, modified by other factors as determined by the Master. In all cases the Master will tell you the TN before a card is drawn. See the conflict chapter for a full description of combat rules.
Combat Example, Chuk vs Klackons
While his partners make their escape, Chuk drops to a knee and points his blast MMG down the hallway. He knows the klackons are close on his tail, the unnerving clicks of their claws causing his fur to dampen with sweat. After a few very long seconds, two klackon warriors barrel around the corner, and rush toward him. The psychological effects of the click-click-click cause him to hesitate for a moment, just a moment. As they scramble to within a few meters, Chuk unloads.
The range is close for a blast MMG, which makes the TN 5. Because the MMG is a heavy weapon, it only operates in fully automatic mode, so it will be delivering burst 10. The following card (50) is drawn:
Chuk has 4d10 in Blast Heavy Weapons. The results 6, 8, 8, 4 indicate a hit. These klackons just started having a really bad day.
Burst Fire
Some weapons are capable of firing more than one shot in a single action. These weapons use the burst section of the action card. If a hit is scored, check the appropriate burst result to see how many shots hit. Weapons that are capable of firing in more than one mode are assumed to fire the minimum number of shots unless specified otherwise.
The number to the left is the burst value, which indicates the number of projectiles fired. The number to the right, inside the burst icon, is the number of actual hits scored. The difference between the burst value and the number of hits is the number of stray shots (used with optional unintended targets rules). Each hit after the first in a given location increases the damage value of the weapon by 1.
See the action card appendix for more on burst fire results.
Hitting Multiple Targets
The rules for hitting multiple targets with burst fire are not ready for prime time, so no examples will be covered in card usage until they are.
Spreading Hits Across Multiple Locations
As with hitting multiple targets, rules for this are not yet ready. This may or may not be a thing.
Combat Example, Chuk vs Klackons, continued
Standing his ground, Chuck unleashes a withering hail of blast fire into the approaching klackons. How many projectiles find home?
Wow, 8 rounds plow into the lead klackon.
Hit Location
To the left of the cause grid is a set of four rectangles. Each of these contain a hit location.
The second rectangle from the bottom has rounded corners and red font. This is the standard hit location. The other hit locations are used with the optional bump rules (see below) as well as with positional adjustments such as advantages of high ground. Consult the conflict chapter for more on hit locations.
Combat Example, Chuk vs Klackons, continued
Consulting the hit location section of the card, Chuk determines that his rounds hit the left leg.
Armor Penetration/Ablation
Successfully placing ordinance on a target is one thing, penetrating the protection of said target is another. Each weapon has a penetration value and type, as well as tech level. Armor has protection values versus multiple attack types, as well as a tech level. Most natural armors, such as the shell of a turtle, have an effective tech level as well even though they are not technological per se. Many spacefaring creatures have natural armor that has no tech level, these creatures ignore the tech level of all weapons.
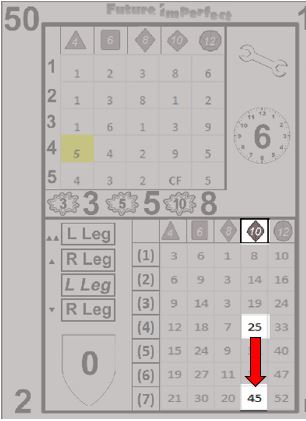
Each action card has a shield icon to the right of the effect grid. Inside the shield is a number from -2 to +2. This number is applied to the penetration value of the attack before comparing it to the protection value of the armor. This is known as the Effective Penetration (EP).
If the EP is 2 or more greater than the protection value of the armor, the attack penetrates. If the EP is equal to or one greater, the attack ablates. If the EP is less than the protection value, the attack deflects.
Attacks that penetrate do full damage. Attacks that ablate do reduced damage. In both cases, the protection value is decremented. Attacks that deflect do no damage and the protection value is unaffected.
Tech Level and Armor Penetration/Ablation
Tech level has some effect on this, but it is yet undetermined.
Burst Fire and Armor Penetration/Ablation
This also might have some effect, but it is also as yet undetermined.
Combat Example, Chuk vs Klackons, continued
Now for the moment of truth. Can the charging klackons withstand the destruction wrought by Chuk and his blast MMG? Blast MMGs are TL 8, Penetration 8, and are energy weapons. Klackons have natural armor (no tech level), protection 6 in chest/belly, 5 everywhere else.
The blast MMG penetrates the left leg, dealing full damage (4)d10. The protection value for this klackon is reduced to 4 in his left leg.
Dealing Damage
Damage is applied exactly as described in complex tasks. The only difference between collecting victories and assigning wounds is that any leftover effect magnitude is applied as concussion.
Combat Example, Chuk vs Klackons, continued
The blast MMG penetrated the leg armor of the klackon, dealing (4)d10. The magnitude is 28.
The shot deals 4 wounds and 4 concussion.
Ancillary Effects
Once all hits are applied, the next step is determining if any other effects occur. There are two possible ancillary effects: equipment failure and unintended targets. Equipment failure is represented by a wrench icon located just below the penetration shield.
If a broken wrench with a number inside of it appears, that number is compared to the reliability of the equipment to determine if a breakage occurs. If an intact wrench appears, this section can be ignored. See the gear chapter for more information on equipment reliability.
The second possible ancillary effect is unintended targets. Before any ranged shot is attempted, the Master will inform the player of any potential unintended targets. Generally, unintended targets are within one meter of the firing path of the weapon. See the Conflict chapter for more on determining potential unintended targets.
Unintended targets that are hit will be covered with an X.
Combat Example, Chuk vs Klackons, conclusion
Now that the damage has been dealt, the remaining possible effects must be determined, if any. First, check for equipment failure.
Since an intact wrench is present, there is no possibility of equipment failure.
Finally, unintended targets. Since the burst size was 10, and 8 shots hit, the number of stray shots is 2. Given that the hallway is empty except for the two charging klackons, there is only one possible unintended target.
The first unintended target icon is not marked with an X, therefore, the other two shots miss entirely.