Future Imperfect - Action Cards
Action cards are at the heart of Future Imperfect. Whenever success is in doubt, action cards will help you determine the result. In this section action card usage will be explained in a step by step manner. For further information about card anatomy, card creation or alternative card usages, see Future Imperfect: Appendix - 1, Action Cards.
Contents
[hide]The Basics
The Action Cards included with Future Imperfect are loaded with data. The sheer density of information may seem daunting at first, yet once their usage is mastered they become simple and quick to utilize. Note that even in the most detailed of actions only a subset of the information contained will be referenced. In most cases only one or two sections will be necessary.
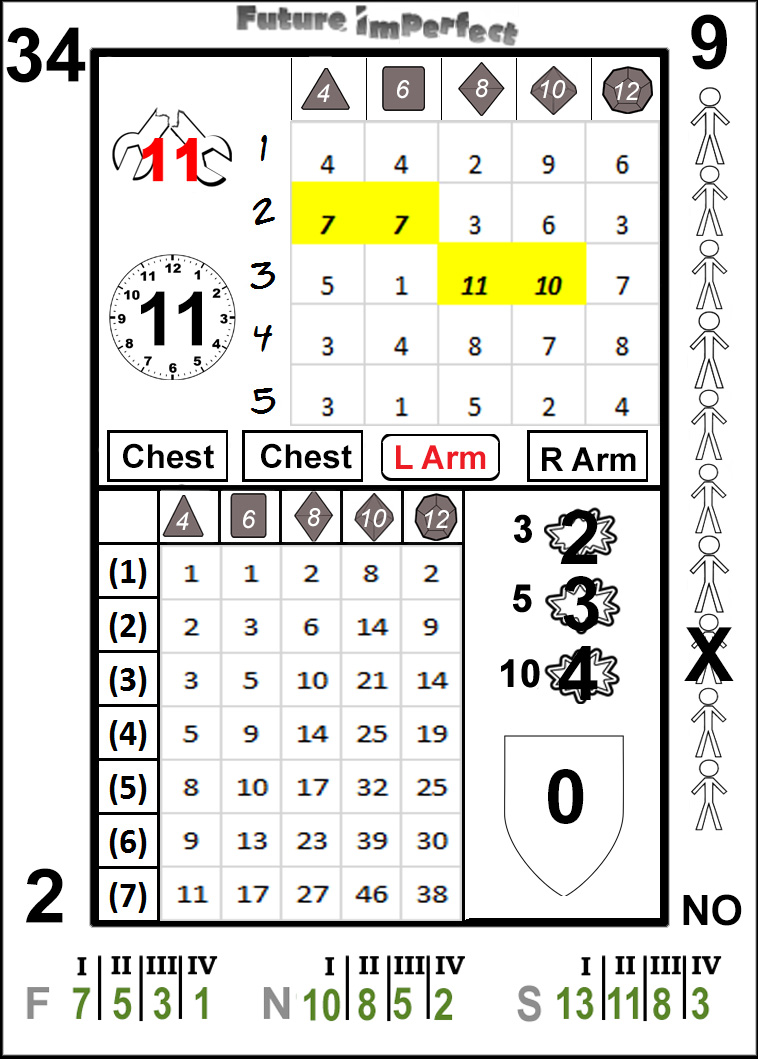
Begin by drawing a card and glancing at the face.
The example card here is number 34. When cards are referenced, the large number in the upper left is the unique identifying number. Since the deck has 54 cards, the cards are numbered 0-53. The numbers in the upper right range from 0-14, with 4 each of 1-13, and one each of 0 and 14. The numbers in the lower left range from 0-5, with 13 each of 1-4, and one each of 0 and 5. The lower right contains yes and no, with 27 of each. Using these card entries is detailed in another section, while the logic behind their distribution is contained in the appendix referenced above.
The Upper Grid: Simple Skill Checks
Skill checks can be performed using only a single result from the card. In the upper section of the card is a 5x5 grid, with rows numbered from 1-5, and columns with 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12, along with symbols matching the shape of dice with the given number of sides.
Do not worry, dice never need to be rolled in conjunction with action cards.
Then why are the dice symbols present? As a player of roleplaying games, you are likely familiar with polyhedral dice. If this is your first roleplaying game, you may have seen the 6 sided cube that is the most common die used in games from table games such as craps to board and roleplaying games as well. The dice symbols help to set expectations for players on what results are likely to occur in a given column. The 6 column, for example, acts like the standard six sided cube. Most results in the 6 column will fall within the range of 1-6, while the results in the 10 column will fall mostly from 1-10. A full explanation for how the results are distributed is available in the appendix linked above.
Each row is an additional die of the appropriate type. When a skill level is greater than one, the player resolving the action may choose any result from a row equal to or less than the level of the skill, in the appropriate column based on the governing trait. The only exception to this is critical failures, discussed in the special section below. For example, if Sid Scorpio has an Essence of d6, and a Bravery of 3, he may choose either 6, 1 or 1 (assuming card 34, above, as the card drawn).
Skill checks are that simple. Draw a card, cross-reference the die type of the appropriate trait with the skill level of the skill being used, and choose the result. In general, the highest result present will be chosen, though there may be reasons why another result is selected. Except in the case of critical failures the active player (the one that drew the card and is resolving the check) may always choose whichever result he wishes.
After completing the check, place the card in the discard pile. Even though only a subset of the information on the card was used, each card is utilized for a single action only. In the case of a simple skill check, from 1-5 rows in a single column will be consulted, nothing more.
Further Examples
Fill this section with more examples of simple skill checks.
Exceptional Results
Great stories are filled with instances of characters performing extraordinary actions. Future Imperfect seeks to simulate this with extraordinary results. Previously, it was mentioned that most results in a given column will fall between 1-n, where n is the number displayed atop the column. In some cases, results that are equal to or greater than that number will be shaded in yellow, bold and italicized*. These are exceptional results.
Exceptional results allow results to be open ended. When one of the squares in the result set meet the criteria above, immediately draw another card and add the value from the corresponding square to the previous result. If another exceptional result is drawn, repeat the procedure until a standard result is drawn.
*See the Appendix referenced above for the rationale behind the symbology.
Exceptional Results, Examples
Fill this section with examples of exceptional results.
Critical Failures
As with exceptional successes, entertaining stories often include spectacular failures. At times even the most skilled individual encounters a set of circumstances that cannot be resolved satisfactorily. Critical failures are results that lead to failure no matter the situation, and often can lead to the most dramatic result possible. Adjudicating critical failures is covered in section, this paragraph is solely concerned with how to read the results on the action card.
In most checks, the player can select any result in the appropriate column up to and including the row of the skill level being utilized. The exception to this is when the exact row/column combination yields a CF result. Note that it does not matter if a CF is in any other location on the card, a critical fail only occurs if the exact box directed by the attribute/skill combination contains CF.
For example, again referring to the 34 card presented above, if Chuk has a 4d12 Strength, and is attempting to lift a heavy bulkhead, he would critically fail. In the event of a critical fail the Master determines a result appropriate to the situation at hand, however any member of the Crew, including the player resolving the card, may make suggestions.
Critical Failures, Examples
Fill this section with examples of critical failures.
Complex Skill Checks: More Than a Binary Result
In some cases, an action requires more than a pass or fail. These actions are called complex skill checks. These types of checks could be due to extended actions (where success is achieved over time such as defeating a complex security system), contests (where two characters compete at a task), actions involving a magnitude rather than a binary success (such as throwing an item for distance) or other possibilities as defined by the Master. Complex skill checks take simple skill checks one step further, and use two sections of the card: the upper grid (like simple skill checks) and the lower grid.
As with simple skill checks, the upper grid is used to determine whether an action is a success. Without a success, no magnitude is generated. The lower grid is used to determine the magnitude, if necessary. An action card is discarded after one resolution.
Using the Lower Grid
Unlike the upper grid, the results in the lower grid are always arranged in order of increasing magnitude as the row increases. The rationale for the arrangement of values in the grids is covered in the appendix linked above. Because of this, the box corresponding to the appropriate row and column is always chosen.